Test Azure AD secured API with Postman
Sacha BruttinImagine that you have a nice API deployed on Azure and secured by Azure AD. For example, we will create a simple Azure Function who return the name of the logged user. Here is the code:
using System.Net;
using System.Security.Claims;
public static async Task<HttpResponseMessage> Run(HttpRequestMessage req)
{
var name = ClaimsPrincipal.Current.FindFirst("name")?.Value;
return name == null
? req.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest, "'name' not found in the claims list!")
: req.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, "Hello " + name);
}
Try to call the Azure Function from Postman you will receive a "You do not have permission to view this directory or page." message with a 401 Unauthorized error code.
This is because we didn’t pass an Authentication header with a valid bearer token. As we are using AzureAD, we are supporting OAuth2.0 authentication and Postman is providing a way to retrieve a valid token without leaving the application. Check https://www.getpostman.com/docs/postman/sending_api_requests/authorization for details.
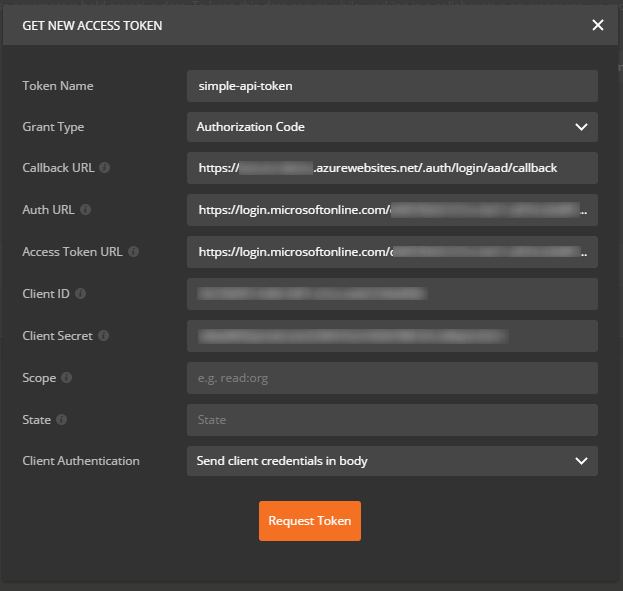
So far, so good. But what are the parameters that we should pass to Postman to retrieve a token? First, we will use the Authorization Code grant type. When you select this grant type on Postman, you will see that the following parameters are needed:
- Callback URL
- Auth Token URL
- Access Token URL
- Client ID
- Client Secret
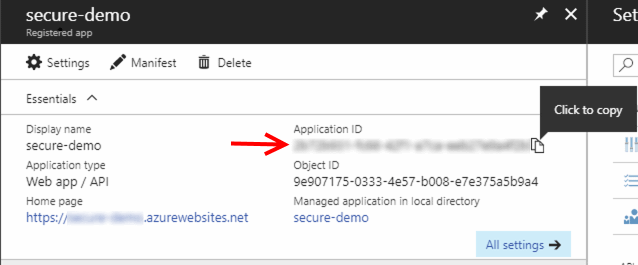
To retrieve these information, open the Azure Active Directory blade and select App registration.
Client ID
The Client ID parameter is know on Azure AD as the Application ID. Open your registered app and copy the value.
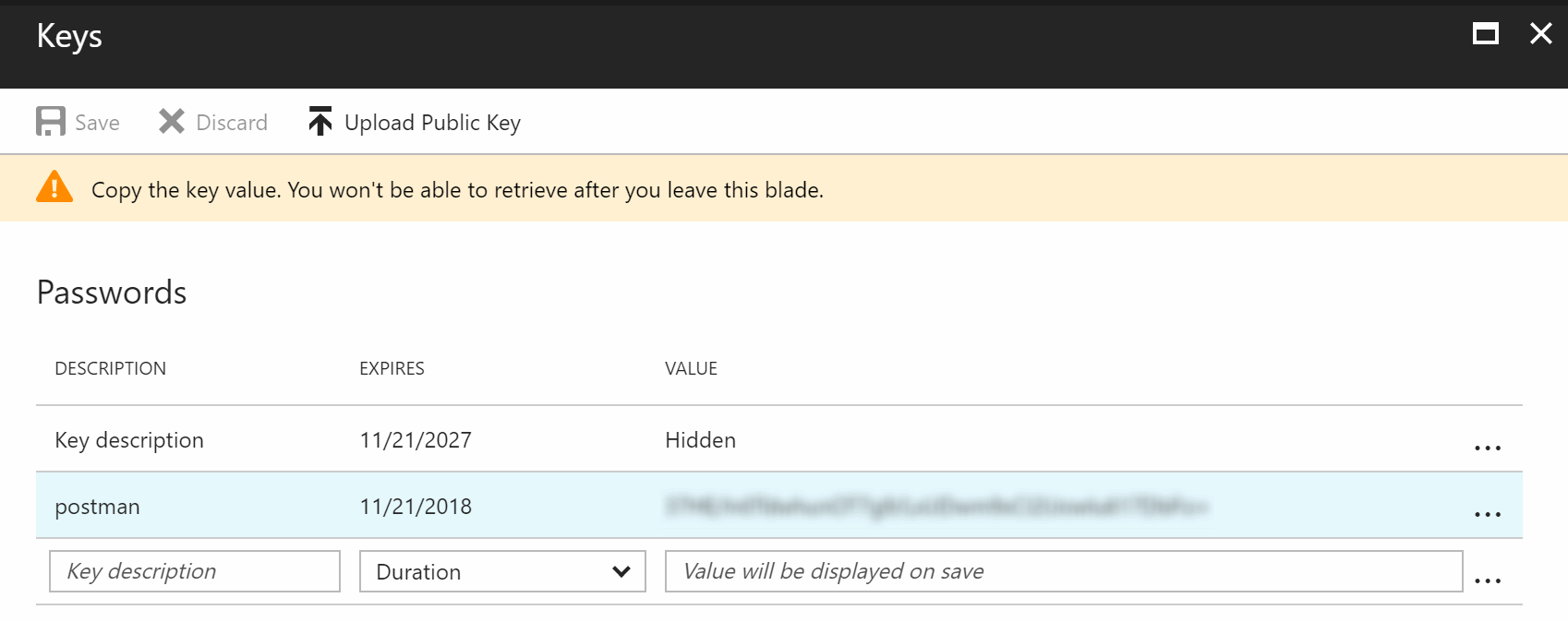
Client Secret
Go to the Keys settings of the Registered App and create a new Password. Write down the generated key when saving, you won’t be able to retrieve it later otherwise.
Retrieve the URLs
The Auth Token URL and Access Token URL can be found by clicking on the Endpoints button. Azure AD requires that you pass the resource you want to access with both urls, so you will need to add ?resource=[application_id] at the end.
| Postman | Azure AD |
|---|---|
| Auth URL | https://login.microsoftonline.com/[tenant_id]/oauth2/authorize?resource=[application_id] |
| Access Token URL | https://login.microsoftonline.com/[tenant_id]/oauth2/token?resource=[application_id] |
To get the Callback URL, check the Reply URLs setting. If you have created the Azure AD Application using Azure EasyAuth, you will have a default value looking like this: https://[appservice-name].azurewebsites.net/.auth/login/aad/callback
Grant Permissions
Before to be able to call the API, you will need to click on the “Grant Permissions” button of the “Required permission” settings. Otherwise, you could get a error message saying:
error=access_denied
error_description=AADSTS65005: Invalid resource.
The client has requested access to a resource which is not listed in the requested permissions in the client’s application registration
Other Parameters
Moreover, you will neeed to set a Token Name of your choice and set Client Authentication to Send client credentials in body. We can leave the Scope and State parameters empty.
Retrieve a token
You are now ready to get a new access token.
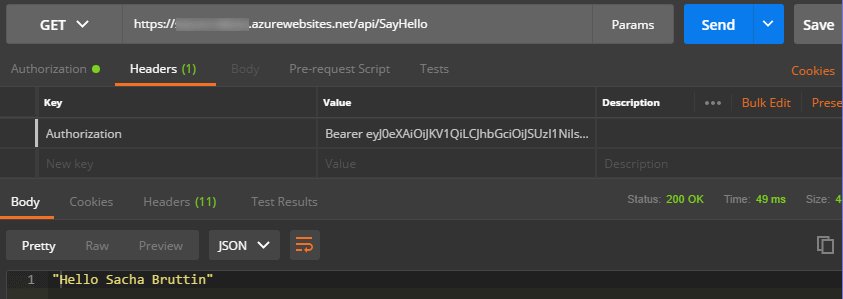
After clicking on “Request Token”, a popup window will prompt you your Azure AD credentials. If you get an issue, start by looking at the Postman console and if you don’t get enought information there launch Fiddler to debug the messages. When everything goes well you recieve a new token that you can add to your request header by clicking on the “Preview Request” button.
Conclusion
You are now able to call your API from Postman and get a nice response.
Don’t forget that an Azure AD Token is valid for 60 minutes only. Request a new token when needed…